In cybersecurity, there’s a growing recognition that perfect defense is impossible. The question isn’t if your organization will face a breach, but when—and how quickly you can recover. This shift from prevention-focused security to cyber resilience demands new approaches, with AI playing a central role in building adaptive, responsive security ecosystems.
Defining Cyber Resilience in the AI Era
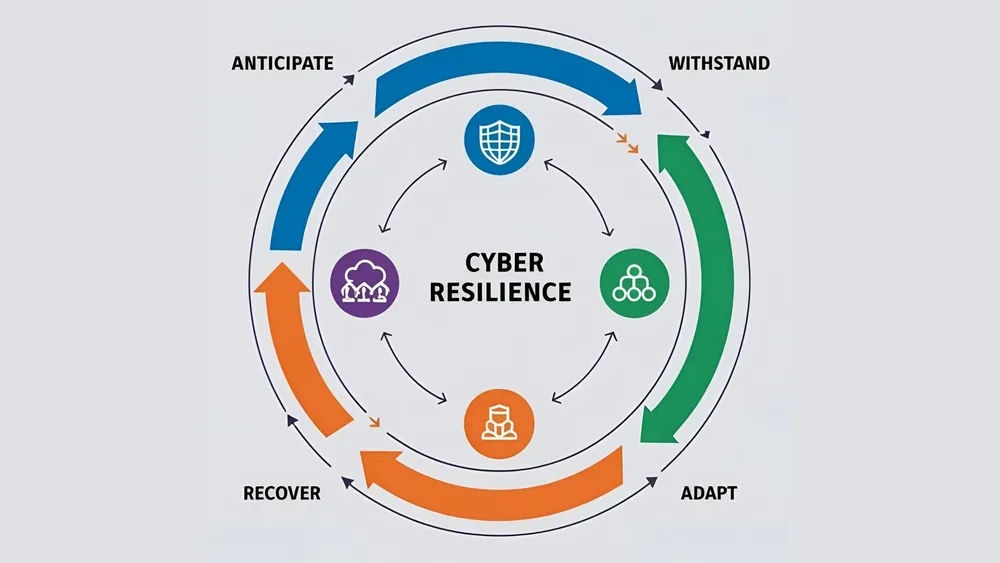
Cyber resilience goes beyond traditional security measures to focus on business continuity despite adverse cyber events. It encompasses:
- Anticipation: Predicting potential threats before they materialize
- Withstanding: Maintaining critical functions during attacks
- Recovery: Quickly restoring operations after incidents
- Adaptation: Learning from each event to strengthen future posture
AI technologies are transforming each of these dimensions, but implementation challenges remain significant.
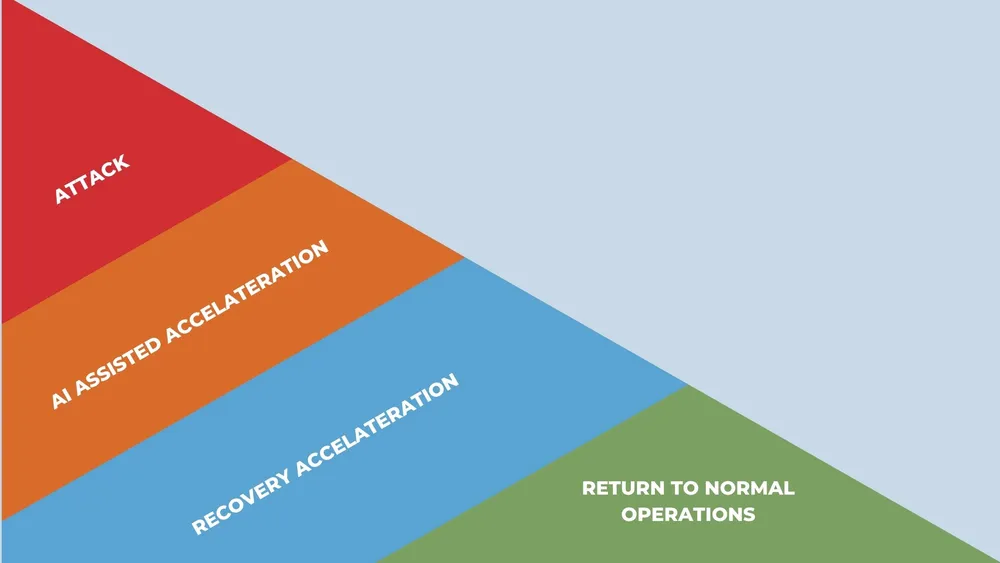
Operationalizing AI for Enhanced Recovery Capabilities
The true test of cyber resilience is how quickly an organization can return to normal operations after an incident. AI systems are revolutionizing recovery in several key ways:
- Automated Containment: Machine learning algorithms can identify affected systems and automatically isolate them to prevent lateral movement, reducing the attack surface during active incidents.
- Intelligent Backup Orchestration: AI-powered backup systems can prioritize critical data restoration based on business impact analysis, ensuring essential services return first.
- Predictive Recovery Planning: By analyzing past incidents, AI can forecast recovery resource requirements and optimize restoration sequences, cutting downtime by up to 60%.
Organizations successfully implementing these capabilities typically establish dedicated recovery teams with clear AI implementation authority, separate from traditional security operations.
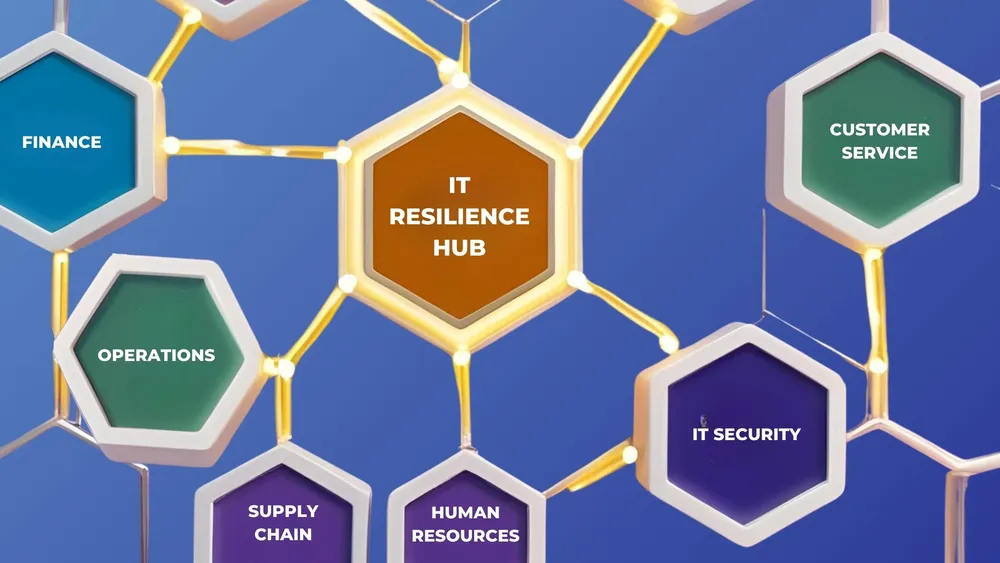
Building Cross-Functional Resilience Through AI Integration
Cyber resilience fails when treated as purely an IT concern. The most successful implementations integrate AI capabilities across business functions:
- Supply Chain Resilience: AI monitoring of supplier systems for early threat indicators
- Customer Service Continuity: Automated failover of customer-facing systems with AI-powered degradation management
- Financial Operations Protection: Machine learning anomaly detection in transaction processing
Each functional area requires domain-specific AI training and implementation approaches, challenging the “one-size-fits-all” security model many organizations attempt to impose.
The Data Quality Imperative in Resilient Systems
AI-powered resilience is only as effective as the data feeding these systems. Organizations struggling with resilience often face these critical data challenges:
- Incomplete Visibility: Security telemetry gaps creating blind spots in resilience planning
- Inconsistent Formats: Data standardization issues hampering cross-system AI analysis
- Historical Limitations: Insufficient incident data for effective AI training
Leading organizations address these gaps by implementing unified data lakes for security information, standardizing logging formats across all systems, and supplementing internal data with industry threat intelligence feeds.
Practical Implementation Framework for AI-Powered Resilience
Moving from concept to operational reality requires a structured approach:
- Resilience Baseline Assessment:
- Map critical business functions and supporting systems
- Establish current recovery time objectives and capabilities
- Identify priority improvement areas based on business impact
- Targeted AI Implementation:
- Deploy anomaly detection for early warning capabilities
- Implement automated response systems for common scenarios
- Develop predictive recovery models for critical systems
- Cross-Functional Integration:
- Embed resilience planning in business continuity exercises
- Establish resilience metrics tied to business outcomes
- Create resilience champions outside IT security
- Continuous Adaptation:
- Analyze actual incidents against AI predictions
- Refine models based on real-world performance
- Regularly simulate new attack scenarios to test resilience
Measuring Resilience Effectiveness
Successful organizations move beyond traditional security metrics to measure resilience through:
- Recovery Time Improvement: Measured reduction in system restoration timelines
- Business Impact Minimization: Decreased financial impact from similar incident types
- Adaptation Speed: Time to implement lessons from incidents into improved defenses
The organizations showing the strongest resilience improvements typically maintain dedicated resilience teams with direct executive sponsorship and cross-functional authority.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
Building true cyber resilience requires rethinking security as a business enabler rather than just a defensive function. AI technologies offer unprecedented capabilities to anticipate, withstand, recover, and adapt to cyber threats—but only when implemented with clear business objectives, cross-functional integration, and continuous measurement against resilience outcomes.
Organizations that successfully navigate this transformation will not only survive the inevitable breaches but will maintain competitive advantage through superior business continuity and stakeholder confidence in the face of escalating cyber threats.






